Monday, October 13, 2014
That 80-20 Rule
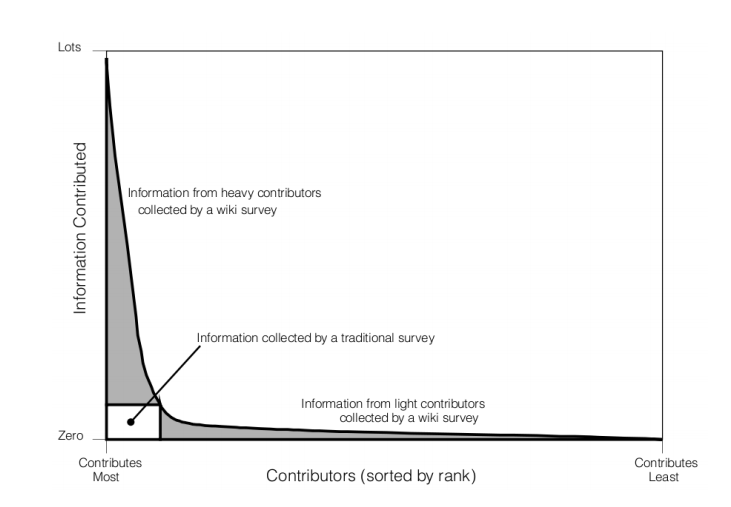
Looks like Wikipedia has its own 1%. I knew that, but this application to surveys is novel and interesting.
Inspired by Wikipedia, Social Scientists Create a Revolution in Online Surveys
Inspired by Wikipedia, Social Scientists Create a Revolution in Online Surveys
Most of the information on Wikipedia comes from a tiny proportion of users. Now social scientists are collecting data in a similar way, allowing participants to design surveys as they contribute. ..... “Just as Wikipedia evolves over time based on contributions from participants, we envision an evolving survey driven by contributions from respondents” ..... a wiki survey. This starts with a set of seed questions but allows respondents to add their own questions as the survey involves. ..... this format allows participants to respond to as many choices as they wish. They call this property greediness. ...... These included ideas that would have been unlikely to emerge through other data gathering methods, such as “Keep NYC’s drinking water clean by banning fracking in NYC’s watershed” and “Plug ships into electricity grid so they don’t idle in port—reducing emissions equivalent to 12,000 cars per ship.” ...... “If Wikipedia were to allow 10 and only 10 edits per editor—akin to a survey that requires respondents to complete one and only one form—it would exclude about 95% of the edits contributed”

Related articles
Environmentalists Continue to Call for Tighter Controls on Fracking
Deep Divide: What are environmental implications of Measure J?
Water control, local jobs, environment top One Cowichan election survey
Plan would limit fracking near western Md. lake
Group urges Md. to ban fracking near Savage River
Trade Agreements Bring Peace
| English: Red (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |

India and Pakistan, take heed.
Network Theory Reveals The Hidden Link Between Trade And Military Alliances That Leads to Conflict-Free Stability
There was a time when historians focused largely on events as the be all and end all of history. But in recent years, there has been a growing understanding that a complex network of links, alliances, trade agreements and so on play a hugely important role in creating an environment in which conflict (or peace) can spread. ..... “The pressure to economize on alliances conflicts with stability against the formation of new alliances, which leads to instability and would suggest chaotic dynamics,” they say. “This instability provides insights into the constantly shifting structures and recurring wars that occurred throughout the nineteenth and first half of the twentieth centuries.” ...... Between 1820 and 1959, there were 10 times as many wars per year on average between each possible pair of countries than between 1960 and 2000 ..... it is the formation of trade links between countries that has created the stability that has prevented wars. ..... there has been a rapid increase in global trade since World War II, not least because of the advent of container shipping in the 1960s. ..... trade provides a reason to maintain an alliance .... these economic considerations reduce the incentive to attack another country since trade will be disrupted ......... a rich family of stable networks ...... the initiating event is a poor predictor of the eventual size of an epidemic, fashion or war.
Related articles
The 'Bitter Truth': Empire and the Death of Liberalism
Familiar Crimes In A Strange New World In Johnston And Greenwood's 'The Fuse: The Russia Shift' [Review]
Liberalism Vs. Empire: The Great Antithesis
Kilburn Manifesto: Rethinking the neoliberal world order
North America is a crime scene: The untold history of America this Columbus Day
Europe And Pakistan: A Partnership In Progress - Analysis
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
