Wikipedia is one of the most well-known and widely used online encyclopedias. Below are its strengths and weaknesses:
Strengths:
-
Comprehensive and Broad Coverage:
- Wikipedia offers extensive information on a vast array of topics, from history and science to pop culture and niche subjects.
-
Free and Accessible:
- Content is free for everyone, and articles are accessible globally in multiple languages.
-
Collaborative Model:
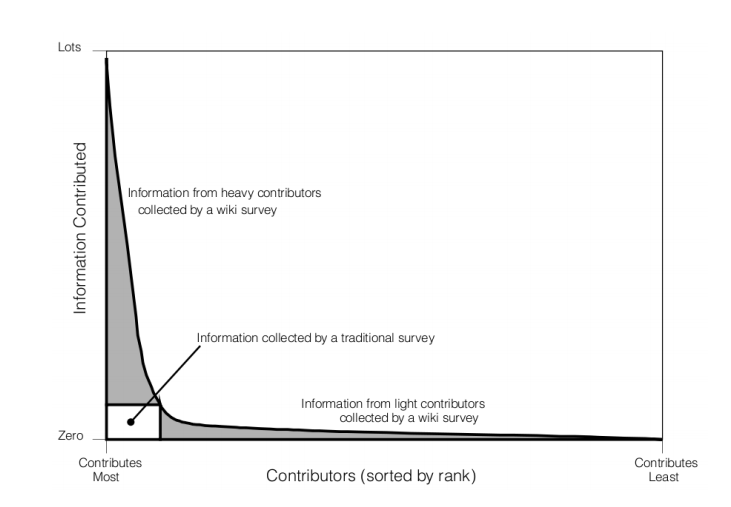
- Thousands of volunteer editors worldwide contribute to and update the platform, which enables rapid updates and coverage of new events.
-
Transparency and Citations:
- Many articles are backed by citations to external sources, allowing readers to verify the information provided.
-
Neutral Point of View:
- Wikipedia strives for neutrality, requiring contributors to present information objectively and without bias.
-
Dynamic Updates:
- Wikipedia can update in real-time, making it a valuable resource for current events and breaking news.
-
Open Data and API:
- Wikipedia provides APIs for developers and open data for researchers, enabling use in various applications.
-
Community Oversight:
- Active contributors and administrators monitor changes to maintain quality and address vandalism.
Weaknesses:
-
Reliability and Accuracy:
- Because anyone can edit Wikipedia, errors, bias, and vandalism can slip through. Articles are not always reviewed by experts.
-
Not Always Neutral:
- Despite policies, some topics (e.g., political or controversial issues) can reflect bias depending on the editors.
-
Quality Variability:
- While some articles are thoroughly researched and well-written, others can be poorly sourced, incomplete, or inaccurate.
-
Dependence on External Sources:
- Wikipedia relies on secondary sources, and the quality of its content depends heavily on the reliability of these sources.
-
Limited Representation:
- Topics about underrepresented regions, cultures, or languages may lack comprehensive coverage.
-
Editor Demographics:
- The majority of contributors are from certain geographic and socioeconomic backgrounds, which may influence coverage and perspectives.
-
Complex Topics:
- Technical or highly specialized topics can be difficult to understand due to jargon or oversimplification.
-
Edit Wars and Vandalism:
- Popular or controversial pages often become battlegrounds for conflicting viewpoints, leading to "edit wars."
-
Over-reliance by Students and General Public:
- Users sometimes treat Wikipedia as an authoritative source rather than a starting point for further research.
-
Censorship and Accessibility:
- In some countries, Wikipedia faces censorship, making it unavailable or selectively accessible.
Conclusion:
Wikipedia's strengths lie in its accessibility, breadth of information, and collaborative nature. However, its weaknesses highlight the need for cautious and critical consumption of its content, particularly for academic or professional purposes. For best use, Wikipedia should serve as a starting point, with further research into authoritative and primary sources for validation.
The business model of Wikipedia, which relies on voluntary donations and unpaid contributions, can be argued to be fundamentally broken for several reasons:
1. Dependence on Voluntary Donations
Wikipedia is funded primarily by donations from its users and philanthropic organizations. This model presents several challenges:
-
Unpredictable Revenue Stream:
- Donations are inherently volatile and not guaranteed, creating financial uncertainty for a platform that serves billions of users worldwide.
-
Underfunding Relative to Value:
- Wikipedia provides immense value as one of the top-visited websites globally, but its revenue is a fraction of what a for-profit entity with similar reach would generate. This mismatch suggests a lost opportunity for sustainable monetization.
-
Donor Fatigue:
- Wikipedia frequently solicits donations from its users. Over time, repeated donation requests can lead to fatigue and declining contributions.
2. No Direct Monetization of Value
Wikipedia’s business model avoids traditional revenue streams like advertisements or premium memberships, which presents significant drawbacks:
-
No Alignment Between Value and Revenue:
- Wikipedia generates no income from the massive data it collects or the extensive time users spend on its platform. Its immense global influence and utility are not reflected in its revenue.
-
Missed Opportunities:
- Alternative monetization strategies, such as paid APIs, premium educational content, or partnerships with academic institutions, are largely untapped.
3. Dependency on Volunteers
The platform relies on unpaid volunteers for content creation, editing, and quality control, creating several structural issues:
-
Burnout and Sustainability:
- Volunteers often experience burnout, and the lack of financial incentives limits long-term commitment.
-
Skewed Contributor Demographics:
- The majority of contributors come from specific regions and socioeconomic backgrounds, leading to biases and uneven content quality across different topics.
-
Inefficiency and Accountability:
- Volunteer-driven contributions can lead to inefficiencies, lack of accountability, and varying standards of quality.
4. Vulnerability to External Threats
-
Legal and Censorship Risks:
- Wikipedia's non-commercial stance does not protect it from legal challenges or government censorship, which could threaten its operations in key regions.
-
Competition:
- Other platforms, like YouTube, Google, and OpenAI, are leveraging monetization strategies to build superior knowledge platforms. Wikipedia risks being outpaced by these competitors.
5. Lack of Incentives for Innovation
-
Stagnation in User Experience:
- Wikipedia has seen minimal changes in its interface and user experience over decades, as there is limited financial motivation or budget to innovate.
-
No Reward for Contributors:
- Contributors are not incentivized with monetary rewards or recognition, which stifles motivation to create high-quality, professional-level content.
6. Overreliance on Goodwill
Wikipedia’s model assumes the goodwill of its users and contributors will sustain it indefinitely. However:
-
Goodwill is Finite:
- As user expectations evolve and digital services become increasingly commoditized, reliance on goodwill may not be sustainable.
-
Competitive Market Forces:
- For-profit entities could replicate Wikipedia's core functionality while offering incentives to contributors, creating a more attractive alternative.
Conclusion
Wikipedia’s business model, while noble, is misaligned with the platform’s scale, value, and the modern digital economy. It undervalues the service it provides and its contributors’ work, leaving it financially and structurally vulnerable. A reimagined model that incorporates sustainable monetization strategies—such as ethical advertising, premium content, or contributor incentives—could better reflect Wikipedia’s true worth and ensure its longevity in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
I am interested.
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025
I am interested.
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025
Wikipedia Needs Competition https://t.co/iy7CWQ96sq
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025
Have been tinkering on building world's knowledge in videos.
— Rashmi R (Ray) Padhy (@rashmiranjan) January 14, 2025
The website will be Vidyaa.
Leveraging perplexity would be interesting.
Let's team up. And Vidya is a good name.
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025
Well put. Excited to see this, and happy to help 🔥
— Lex Fridman (@lexfridman) January 14, 2025
Noted. Please help. We are doing this.
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025
Let's team up.
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025
What is your email? Send me your WhatsApp to paramendra at https://t.co/zu7UkaTLKI I already sent an email to Aravind.
— Paramendra Kumar Bhagat (@paramendra) January 15, 2025